Originally Posted At: https://breakingmuscle.com/feed/rss
The lat pulldown and the pull-up are staples across many training programs — sometimes even coexisting within the same workout. Both exercises train the “vertical pulling” movement pattern and can be highly effective for targeting your back muscles, which is why some lifters regard them as nearly interchangeable. Despite how visually similar the movements may seem, they can actually offer pretty significant and distinct benefits.
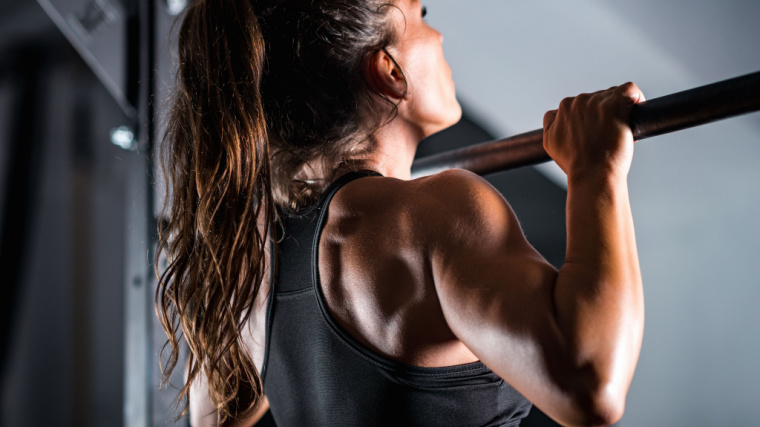

Whether you should focus on pulldowns or pull-ups can depend on a few factors, including your experience and your goals. From technique, programming, and step-by-step execution, here is everything you need to know about these foundational back-building exercises.
Lat Pulldown and Pull-Up
- Exercise Differences
- Exercise Similarities
- Technique Differences
- How to Do the Lat Pulldown
- How to Do the Pull-Up
- When to Program the Best Pulling Movement for Your Goal
Exercise Differences
Recognising the differences between the lat pulldown and the pull-up can put you on the fast track for better results. Some key differences involve the equipment used, or lack thereof. Some relatively subtle, but significant, differences in programming can also be found.
Human Body vs. Machine
The major visual difference between the lat pulldown and pull-up is the fact that one is a bodyweight exercise and the other requires a full cable station. This brings with it two major considerations.
The lat pulldown uses a specialized cable stack pulley system to anchor your body in place while you move an adjustable weight stack, whereas the pull-up simply requires a fixed overhead bar that can support your body weight.
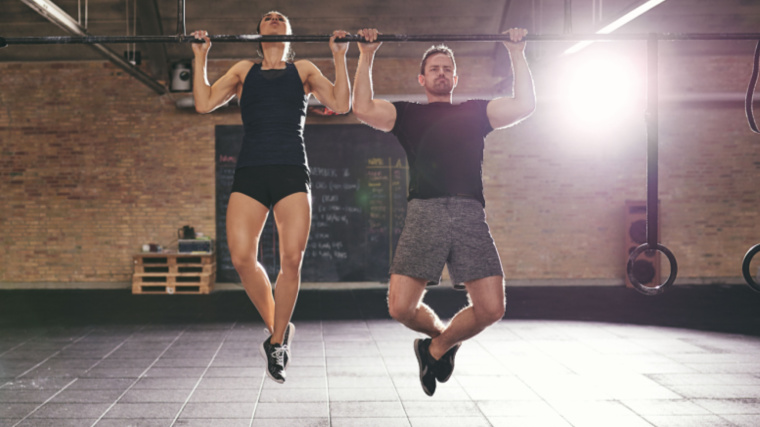

This can affect the relative ease of implementing each exercise into your program based upon availability of equipment, as well as your own capabilities — body weight pull-ups may be too challenging for beginners, while pulldowns can accommodate lifters of any experience or strength level.
As a calisthenics exercise, the pull-up places a greater stabilization challenge on your entire body, from your back and shoulders through your core to your lower body. The stable machine and fixed anchor points provided by the pads on a lat pulldown machine make it tremendously easier to take a seat and get to work. The machine itself provides stabilization, so you can focus targeting your back muscles.
Loading
One of the largest differences between the lat pulldown and pull-up is the range of resistance you can use. The lat pulldown is a highly adjustable machine that simply requires you to add more plates or lower the pin on the weight stack further and further — sometimes exceeding a comparable pull-up load.
The lat pulldown is more scalable than a pull-up — the resistance can be quickly and easily reduced to allow relatively weaker lifters to perform the exercise. Aside from getting creative using resistance bands to assist a pull-up or having access to a dedicated assisted pull-up machine, it can be quite challenging to overcome the baseline level (your body weight) needed to perform a pull-up. This is especially true if you want to perform multiple repetitions per set.
Sets and Repetitions
Similar to the differences in loading, the lat pulldown and pull-up are often paired with distinct set and repetition schemes. For many people, the pull-up is an upper body strength movement that lives in a lower repetition range. Whereas, the lat pulldown typically exists as an effective muscle-building tool that thrives with more moderate repetitions.
You’ll often see pull-ups performed for two to three sets of anywhere from one to 10 repetitions. While the pulldown could be performed with much heavier weights for low-rep sets, it’s nearly impossible to maintain strict form with such programming due to poor leverage. Having your lower body and core locked into position becomes a limiting factor.
In contrast, a lat pulldown is typically done for two to four sets of eight to 12 repetitions. Reaching that type of volume with pull-ups is typically reserved for experienced lifters of a significant strength level, either performed with added weight or with body weight alone.
Exercise Similarities
While there can be several key differences, the lat pulldown and pull-up do share some significant overlaps to consider, as well. They will hit many of the same primary muscle groups, both require some degree of overhead mobility, and the exercises share many basic variations.
Muscles Worked
The lat pulldown and pull-up primarily target your latissimus dorsi — a large swath of muscle located on either lateral side of your back. While the latissimus dorsi (lats) are the prime mover, both exercises will also heavily involve your upper back, biceps, and varying degrees of core musculature to stay in an efficient pulling position.
Mobility Requirements
The vertical pulling pattern used in both exercises requires you to be able to successfully, comfortably, and safely get your arms fully extended overhead. While that may sound simple enough, shoulder mobility and joint health is a very important component of avoiding training-related aches or pains in the long-term.
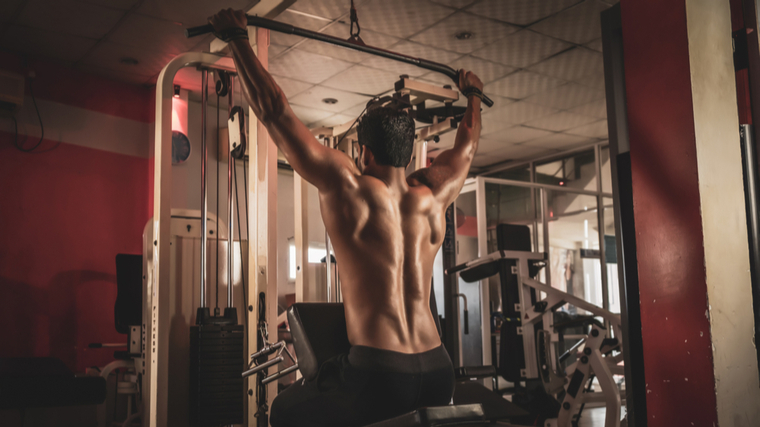

If you can achieve the overhead position effectively, both the lat pulldown and pull-up can be effective at maintaining your overhead mobility, especially when you focus on working through a full range of motion in the stretched (overhead) position.
Grip Variations
When it’s time to introduce exercise variety, the lat pulldown and pull-up can both allow narrow or wide hand positions, which can alter the muscle emphasis from your lats to your upper back or even your biceps. (1)
Both exercises can also be performed using unique grip orientations, from neutral-grip to overhand or even freely rotating (using individual handles or straps to allow your wrists to rotate during each repetition). Like grip width, changing the orientation of your hands and forearms is an effective way of altering muscle recruitment by making slight adjustments. (2)
Technique Differences
The lat pulldown and pull-up have some definitive technique differences. Because one is a calisthenics exercise and the other is performed while seated on a machine, your overall body position will affect exercise technique.
Hollow Body
The hollow body is a full-body bracing technique that helps to create a rigid body posture. The high level of total body tension it creates allows you to better control your movement through space. This technique is especially important during the pull-up, where you will be freely moving without any anchor points aside from your grip.
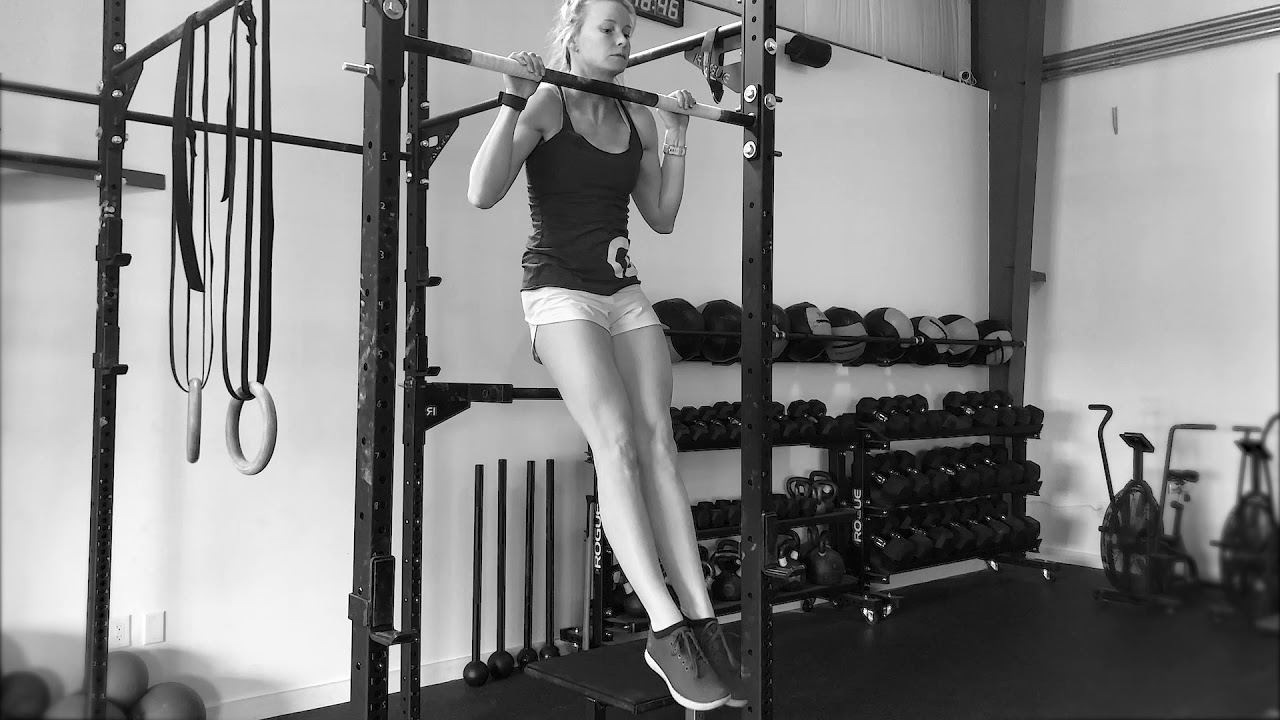

In order to successfully perform a pull-up, establishing a strong hollow body technique is essential to maintain stability. The lat pulldown, on the other hand, provides this stability on your behalf by offering leg pads to hold you in place.
Torso Angle
Your torso angle during each repetition is a major difference between the pull-up and lat pulldown. Because your lower body is secured under the knee pads, the lat pulldown allows you to manipulate your torso angle to target subtly different muscles. A greater degree of backward lean could emphasize more of your upper back, whereas a more vertical torso angle puts your upper back into a less advantageous position and emphasizes lat activation.
On the other hand, fairly consistent technique and upper body position is required for a proper pull-up. From a dead-hang position (gripping the bar with your arms fully straightened), you must set your shoulder blades by first “shrugging” yourself up. In doing so, you will be able to better leverage your latissimus dorsi to complete the rep and actually pull you up.
When you get this technical cue right, you will have a slightly backward-leaning torso angle while performing each repetition, but nowhere near the freedom of motion provided by the lat pulldown machine.
Lower Body Position
Your lower body positioning will certainly be a notable difference in each exercise. Similar to the stability requirements during the hollow body technique in the pull-up, your leg position will be affected by the need to stay rigid. Fully lock your legs out, leaving them either hanging straight down or angled slightly ahead of your body. You cannot achieve a strong, stable hollow body position with bent legs.
With a lat pulldown, you will be in a completely seated position with your feet flat on the ground driving your knees up against the pad. While some lifters disregard the knee pad and let their heels leave the ground during pulldowns, this poor form doesn’t add any benefit and only reduces your stability and upper body pulling power.
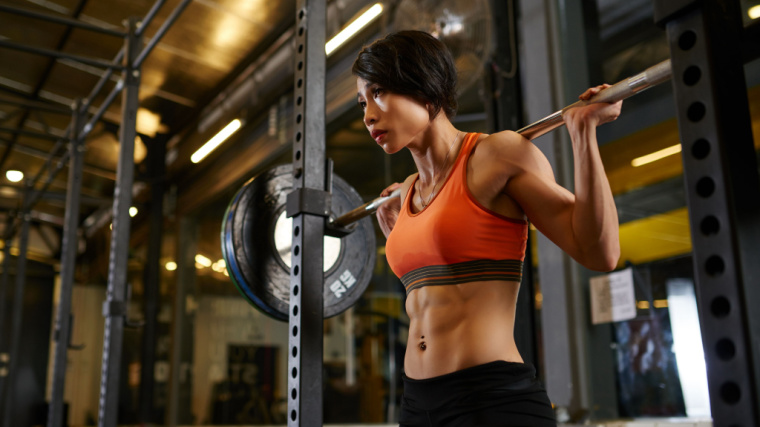
How to Do the Lat Pulldown
Sit on the lat pulldown machine and adjust the knee pads to snuggly anchor your legs in place with your feet flat on the ground. Stand back up and grab the lat pulldown bar evenly, about shoulder-width apart, with an overhand grip.
Brace your full body and sit down, securing your legs under the knee pads. Squeeze the bar tight, brace your core, drive your legs into the knee pads by performing a static calf raise.
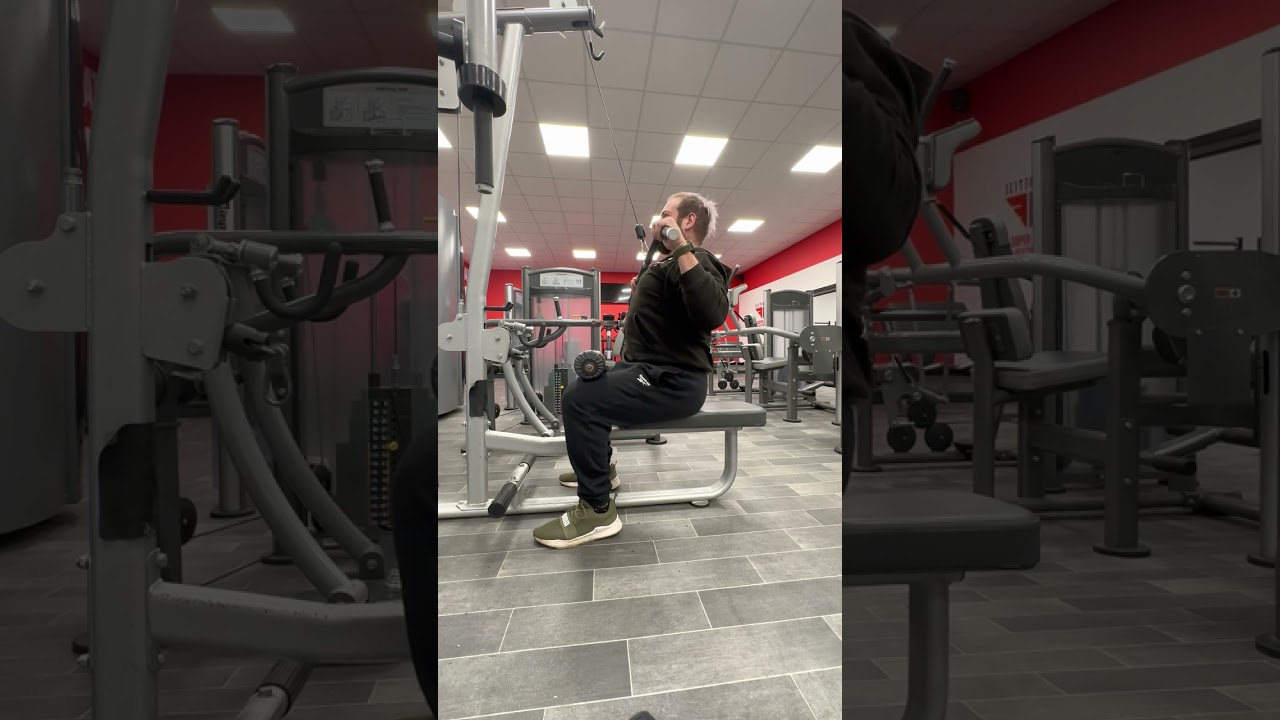

Lean back slightly and pull the bar toward your chest. Focus on feeling your back squeeze in the bottom position before straightening your arms to return to the starting position.
Form Tip: Be diligent to avoid momentum. Secure your body in the machine and brace hard – only move the bar by squeezing your back and pulling with your arms. Do not excessively sway your torso backwards.
Benefits of the Lat Pulldown
- The lat pulldown has a high degree of stability, making it a more effective way to focus on the back muscles.
- The pulldown machine offers highly scalable loading, making it easy to perform for lifters of all experience levels.
- Multiple handle attachments allow many variations for different benefits.
- It’s relatively safe to take this exercise close to muscle failure.
Lat Pulldown Variations
The majority of effective lat pulldown variations will capitalize on different handle attachments to slightly change your technique and alter muscle recruitment.
Close-Grip Pulldown
Close-grip pulldowns draw your hands slightly closer together than the standard, shoulder-width grip. This increases the amount of leverage your lats have and slightly increases the range of motion — both of which can lead to a stronger training stimulus.
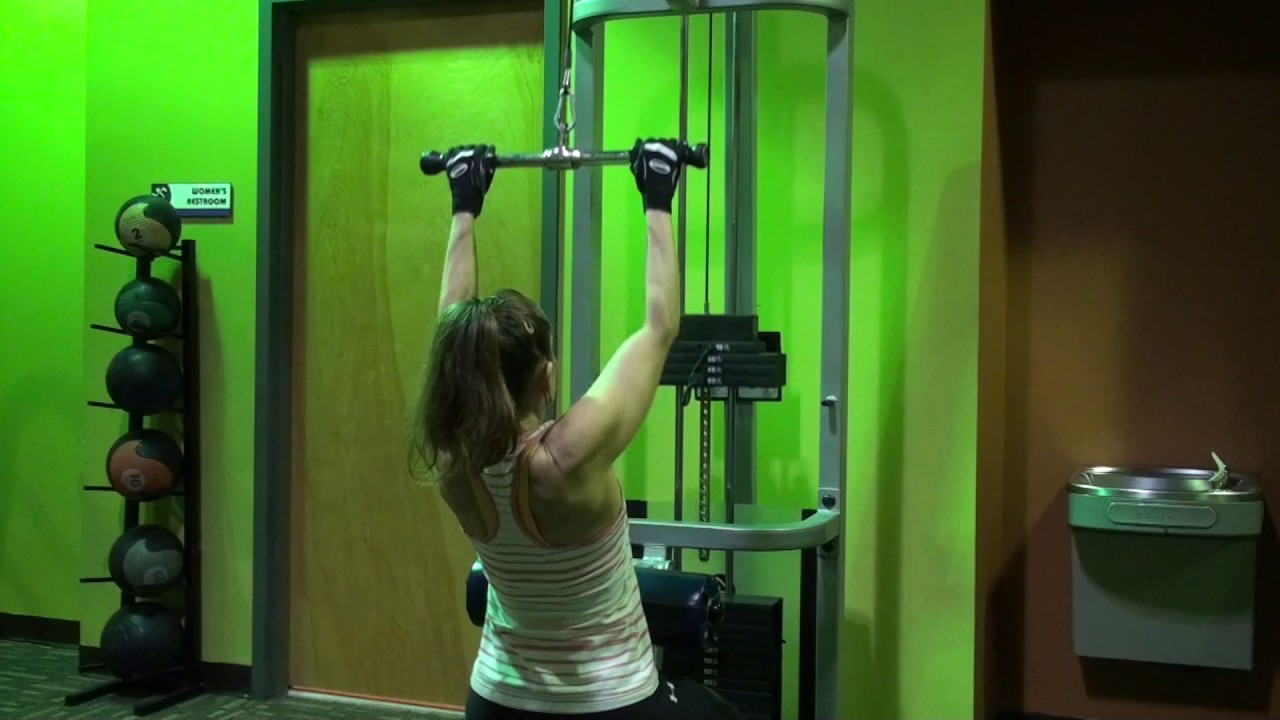
The close-grip pulldown can make the exercise more effective when you’re just learning general technique by delivering a strong training stimulus without needing heavy weight.
Wide-Grip Pulldown
Wide-grip lat pulldowns place your hands slightly farther apart than the standard issue grip placement. This will put your lats at a greater disadvantage, making some of the supporting musculature in your upper back, shoulders, and arms contribute more. This will also reduce the load you’ll be able to lift.

This is a great exercise to fill gaps in your physique or in your strength development. By strengthening relatively weaker links, wide-grip pulldowns can also prolong the amount of time you can make progress before adding weight.
Dead-Hang Pulldown
The dead-hang style of lat pulldown will have you fully “relax” your shoulder blades and assume a completely upright torso between each repetition. Your teres minor (a small shoulder muscle) will get some added work helping to stabilize your shoulder for each repetition.

This is a great way to gain, and maintain, shoulder stability. The increased muscle recruitment will also help upper back development.
Single-Arm Pulldown
The single-arm lat pulldown turn the exercise into a unilateral (single-sided) version. This forces each side of your body to work independently of the other, which will greatly help to accommodate any body size or shape while addressing any natural asymmetries.
The single-arm pulldown is also a tremendously effective way to add more progression time to your lat pulldown exercise by essentially doubling the amount of load each side will have access to.
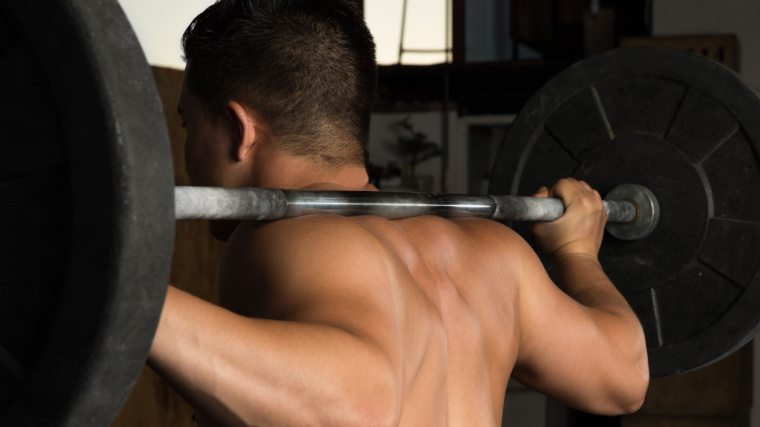
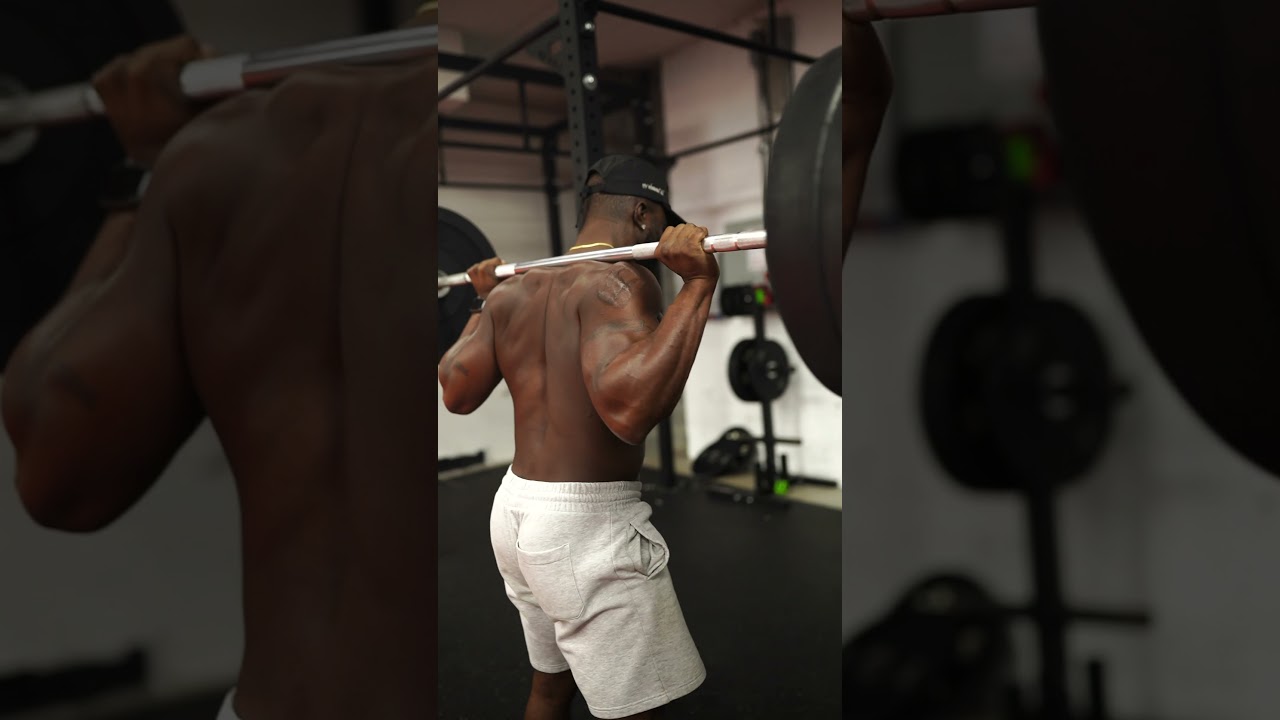
How To Do The Pull-Up
Perform the pull-up by grabbing a straight bar that is high enough for your legs to dangle freely without touching the ground. Use a small box or (safely) jump to grab the bar with an overhand grip approximately shoulder-width apart.
Perform a hollow body technique by flexing your core, depressing your shoulder blades, engaging your glutes, and locking your quads.
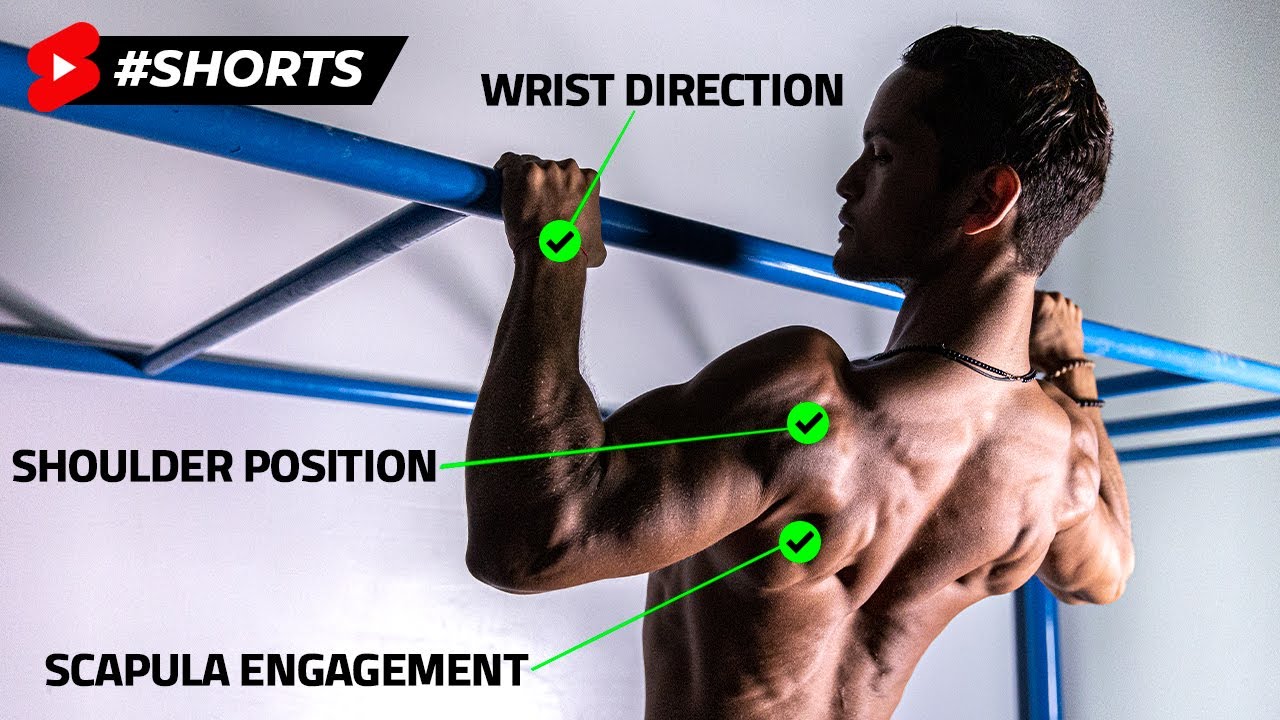
Engage your lats and flex your arms to pull your chest toward the bar. Once you have reached the highest point that you can pull yourself to, slowly lower back to the starting position using control. Maintain your brace and perform for your target repetitions.
Form Tip: Be diligent about maintaining hollow body tension and eliminating any lower body sway. Performing a pull-up gets exponentially more difficult when you have to counter any unneeded movement. Stay braced and aim to start each repetition from a motionless position. Swinging your hips and legs may help you perform more reps, but it reduces muscular stress on your back.
Benefits of the Pull-Up
- The pull-up requires little-to-no equipment.
- Bodyweight exercises can improve coordination and proprioception (body awareness) which can carryover to general athleticism.
- Scalable to suit either strength or hypertrophy goals when appropriate programming and loading is used.
Pull-Up Variations
Pull-ups can be modified to attack a few different goals. Similar to pull-ups, changing your grip position can deliver some unique benefits.
Wide-Grip Pull-up
Wide-grip pull-ups place your upper back (teres minor) on blast. A wider grip will make it harder on your lats, but also put a bigger emphasis on your ability to maintain the right shoulder positioning for each repetition.
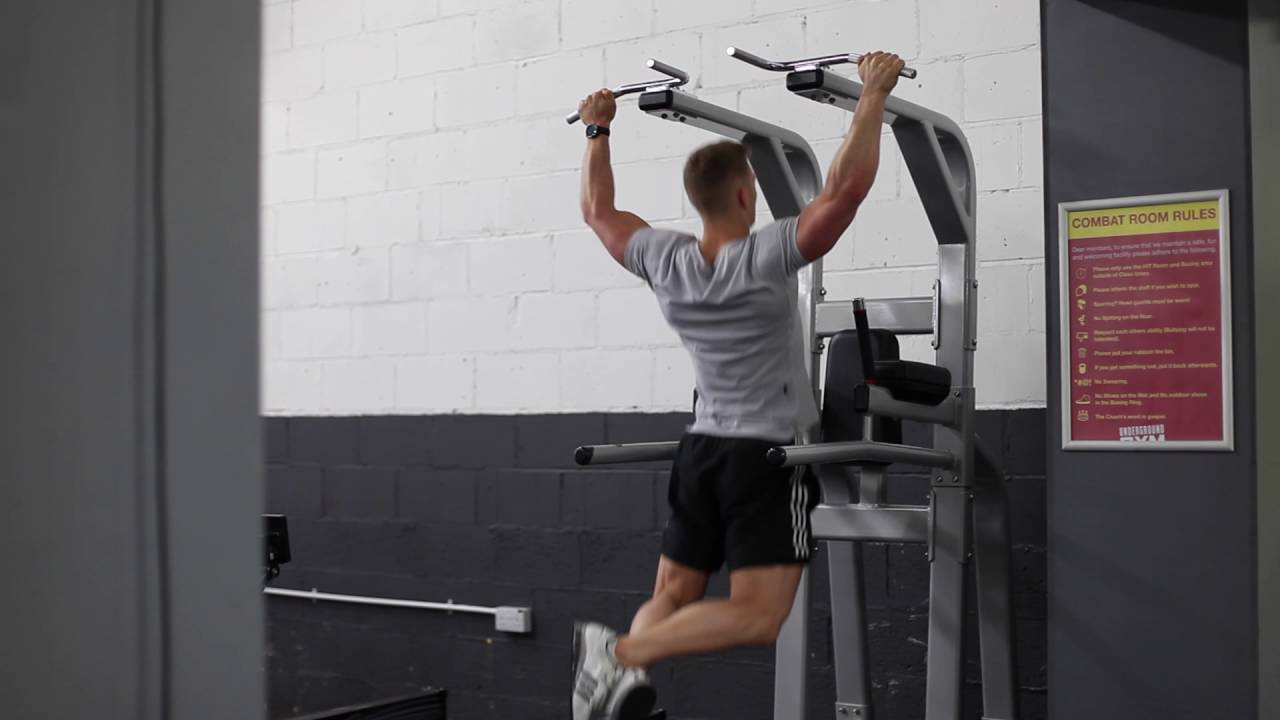

When you’re looking to train nearly your entire upper body, while also seriously roasting your shoulder stability, use the wide-grip pull-up.
Neutral-Grip Pull-up
On the opposite side of things, a neutral-grip pull-up places you in a much more inherently stable position. The relatively closer grip and neutral (palms facing in) hand placement will make it easier to harness your back muscles to pull you up, but also take some of the shoulder stability challenge away.

When you’re looking to go for moderate or higher reps, or build a foundation of strength and muscle, neutral-grip pull-ups are a great option.
Towel Pull-up
Towel pull-ups are a huge boost to your grip strength. This low-tech modification, draping a simple (but sturdy) towel over a bar, will seriously challenge your ability to simply hang on.
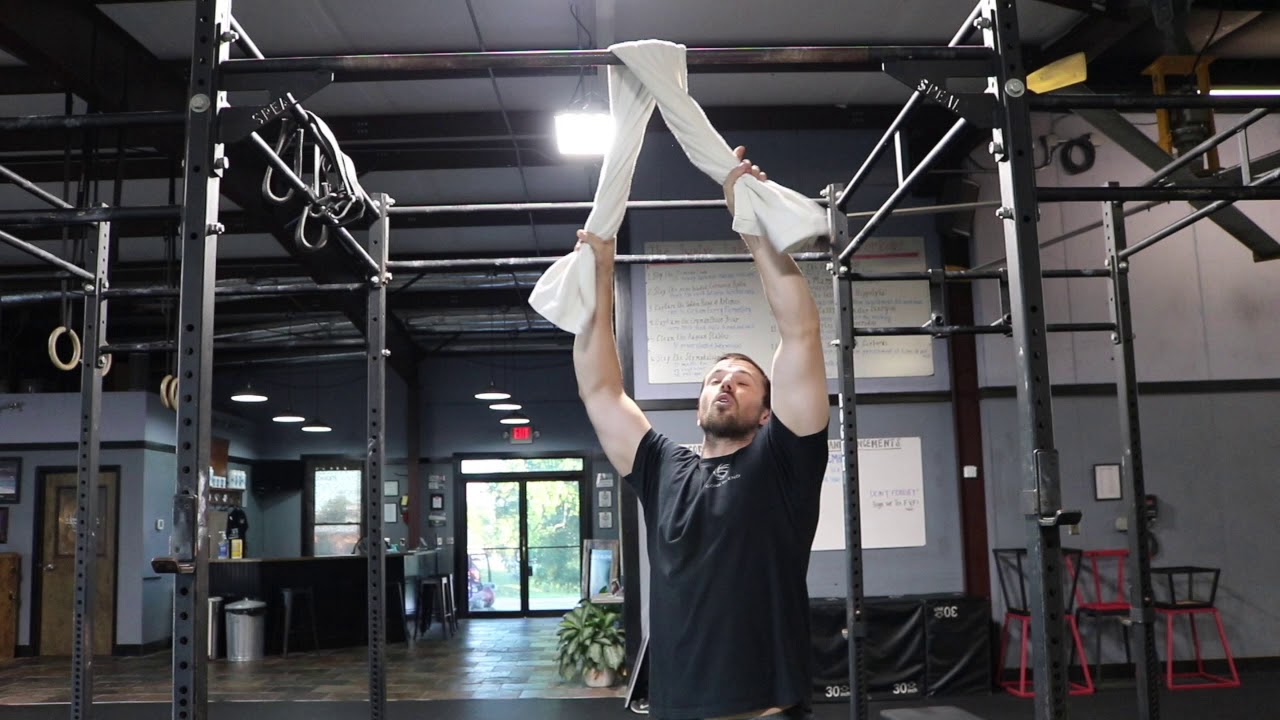

If you’re in the market for a stronger grip and bigger arms — and if you can already perform more than a handful of pull-ups — challenge yourself with towel pull-ups.
When to Program the Best Pulling Movement for Your Goal
There are several instances where either the lat pulldown or pull-up might be the better option. Your specific goals and training experience are unique factors to consider.
Beginner
When you’re a beginner, you’ll be looking to build a base of muscle and strength before eventually launching into a more structured and challenging program. With that in mind, you may struggle with pull-ups because they can be very unforgiving.
While there are ways to make pull-ups more accessible for beginner lifters, such as using resistance bands for assistance, oftentimes a pull-up is a bit of a tall order. Instead, spending some time building a super-strong lat pulldown can be a relatively lower barrier to entry. Once you’ve accomplished this, either option is freely available and effective.
Muscle Gain
Both the lat pulldown and pull-up can be very effective muscle-building tools, but there are some subtle differences that likely edge the lat pulldown ahead. The lat pulldown is a more stable training tool. This means that there will be less “moving parts” in your way while you chase highly stimulating sets that accumulate volume needed to build your back. (3)
The lat pulldown also allows for a slow, controlled, and incremental increase in loading which once again provides a boost to long-term muscle growth. The pull-up is great in its own right, but it’s hard to beat the lat pulldown for pure muscle gain.
Strength Gain
Gaining strength can be accomplished with both the lat pulldown and pull-up. However, the lat pulldown can more easily be loaded and trained for strength-focused results. With that in mind, it’s going to offer you more lat-specific strength.
On the other hand, the pull-up, as a bodyweight exercise, is more of a full-body exercise. In this instance, the pull-up will help build greater full-body strength. If you want better overall strength potential, emphasizing the pull-up will likely be the better option.
Limited Equipment
When you don’t have access to a gym, the choice is a simpler one. The lat pulldown literally requires a machine, which likely is only accessible through a commercial or home gym equivalent.
While a pull-up bar may seem mandatory for doing pull-ups, it is not actually required. A pull-up can, technically, be performed anywhere you have access to a strong, stable anchor point to safely grab. The pull-up wins when you have limited equipment.
Advanced Athlete
If you’re an advanced athlete in nearly any sport, it’s a toss up. Once you’ve developed a strong base of muscle, strength, and coordination, both the pull-up and lat pulldown can be tailored to your needs.
Both can be loaded and progressed, both have unique variations to prolong your progress, and both are relatively easy to master after a short amount of focused time. Depending on your goals or needs, either the pull-up or lat pulldown (or even both) can be effectively programmed for athletic goals.
Prioritize Your Pulls
The lat pulldown and pull-up are both iconic staples of weight training. The exercises have unique benefits, times of superiority, and some clear drawbacks. Depending on your training age, goals, and available equipment, one option may jump out as the obvious choice. Review the information and make the best decision for your goals. Prioritize your pulls for some big gains and, one day, both classic movements may find their way into your program.
References
- Andersen, V., Fimland, M. S., Wiik, E., Skoglund, A., & Saeterbakken, A. H. (2014). Effects of grip width on muscle strength and activation in the lat pull-down. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 28(4), 1135–1142. https://doi.org/10.1097/JSC.0000000000000232
- Signorile, J. F., Zink, A. J., & Szwed, S. P. (2002). A comparative electromyographical investigation of muscle utilization patterns using various hand positions during the lat pull-down. Journal of strength and conditioning research, 16(4), 539–546.
- Schoenfeld, B. J., Contreras, B., Krieger, J., Grgic, J., Delcastillo, K., Belliard, R., & Alto, A. (2019). Resistance Training Volume Enhances Muscle Hypertrophy but Not Strength in Trained Men. Medicine and science in sports and exercise, 51(1), 94–103. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0000000000001764
Featured Image: Tom Wang / Shutterstock
The post Lat Pulldown vs. Pull-Up: The Battle for a Bigger Back appeared first on Breaking Muscle.














 In today’s world, we pretty much always have to wear shoes. But the majority of shoes people wear run directly counter to the way our feet and lower bodies are designed to function. Tall heels, thick padding, restrictive material that allows no movement, heavy sole that prevents us from feeling the ground—modern shoes are monstrosities that cut us off from the world around us and inhibit our ability to navigate it pain-free. Shoes that emulate the barefoot experience on the other hand offer tangible benefits to your health, wellness, athletic performance, and overall well-being by recreating the environment under which the human foot evolved.
In today’s world, we pretty much always have to wear shoes. But the majority of shoes people wear run directly counter to the way our feet and lower bodies are designed to function. Tall heels, thick padding, restrictive material that allows no movement, heavy sole that prevents us from feeling the ground—modern shoes are monstrosities that cut us off from the world around us and inhibit our ability to navigate it pain-free. Shoes that emulate the barefoot experience on the other hand offer tangible benefits to your health, wellness, athletic performance, and overall well-being by recreating the environment under which the human foot evolved.
 For now classes are 6pm and 640pm at 2840 Wildwood st in the Boise Cloggers studio.
Book your class NOW!
click this ==>
For now classes are 6pm and 640pm at 2840 Wildwood st in the Boise Cloggers studio.
Book your class NOW!
click this ==>








